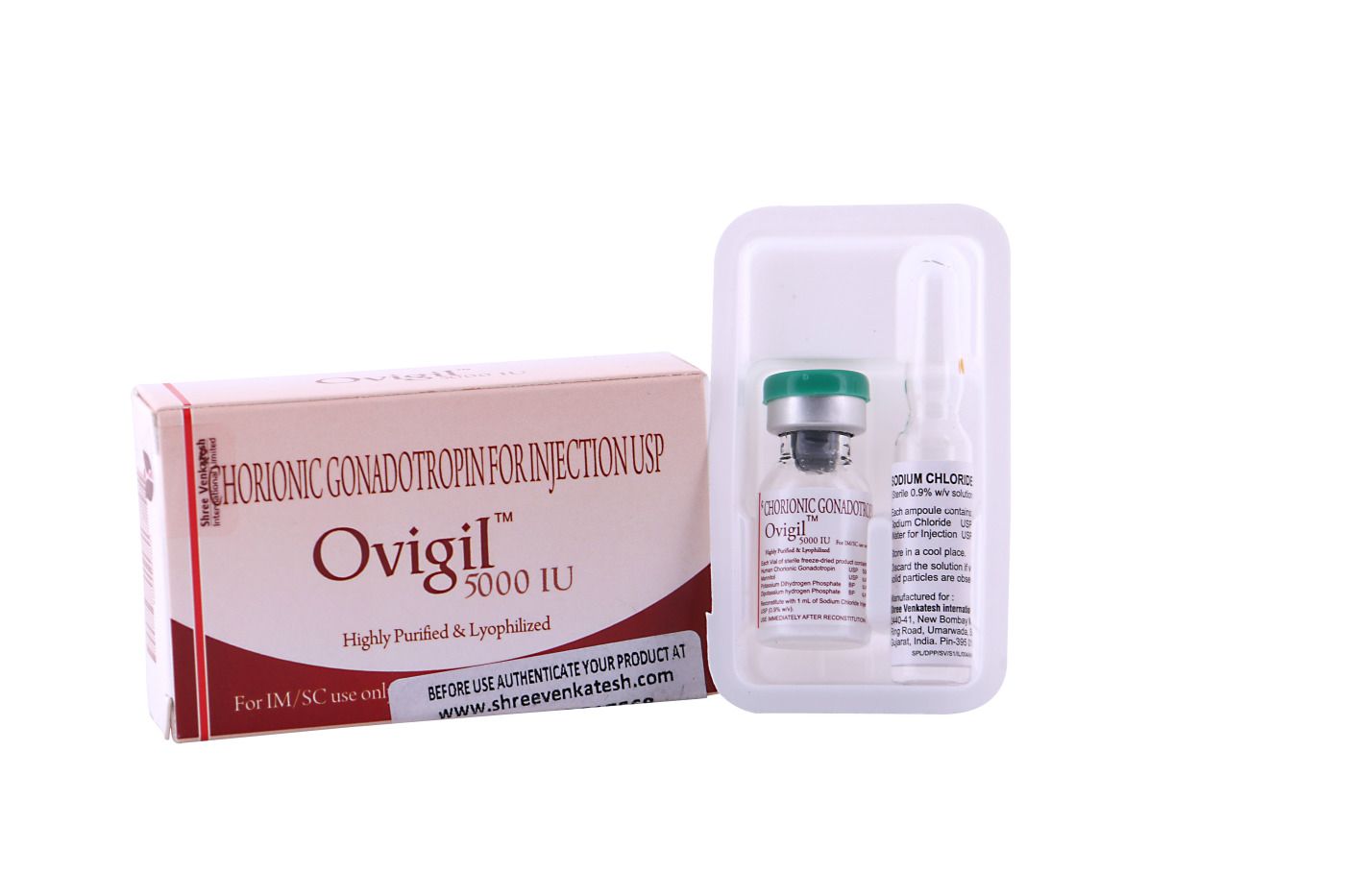
Ovigil – 5000 I.U.
Original price was: 109,00€.89,90€Current price is: 89,90€.
Description
One of the most popular drugs on the market is HCG, often mistaken for HGH or anabolic steroids. It is extremely effective during a cycle, but is also of particular interest in post-cycle therapy to boost natural testosterone production and reverse testicular atrophy.
HCG is not an anabolic steroid, but a protein hormone that is naturally formed in the placenta of, for example, pregnant women. HCG is produced in the placenta immediately after implantation of the fertilized egg in the uterine lining. It has luteinizing properties and is similar to the luteinizing hormone (LH) in the anterior pituitary gland. In the first 6 – 8 weeks of pregnancy, the HCG formed enables the uninterrupted production of estrogens and progestins in the corpus luteum. Later, the placenta itself produces these two hormones. HCG is made from the urine of pregnant women because it is excreted unchanged from the blood in the woman’s urine after it has passed through the kidneys. Commercially available HCG is sold as a dry substance and is used by both men and women. In women, it enables ovulation because it influences the development of the egg cell in the last stage and thus stimulates ovulation. It also aids in the production of estrogens in the corpus luteum.
HOW HCG (HUMAN CHORIONGONADOTROPIN) WORKS:
The fact that exogenous HCG, as mentioned, has almost identical properties to the luteinizing hormone LH produced in the pituitary gland makes HCG very interesting for athletes.
In men, luteinizing hormone stimulates the Leydig cells in the testicles. This in turn radically stimulates testosterone production. For this reason, athletes take injectable HCG to increase testosterone production. HCG is often taken in conjunction with anabolic and androgenic steroids during or after a steroid cycle. As mentioned, taking oral and injectable steroids at a certain level and duration leads to negative feedback. A signal is sent to the hypothalamic-pituitary system because the hypothalamus is receiving the wrong signal from the steroids. The hypothalamus, in turn, signals the pituitary gland to reduce or stop producing FSH (follicle stimulating hormone) and LH. In this way, testosterone production dwindles as the testosterone-producing Leydig cells in the testes are no longer adequately stimulated due to decreased LH. Since the body normally takes a certain amount of time to get testosterone production going again, the athlete experiences a difficult phase after stopping the steroid preparations, which is often accompanied by a noticeable loss of strength and muscle mass. Using HCG immediately after steroid treatment helps to improve this condition because HCG increases testosterone production in the testicles very quickly and reliably. In the case of testicular atrophy, i.e. the shrinking of the testicles, caused by high doses and very long intake times, HCG helps the testicles to regain their original size very quickly. Because occasional injections of HCG while on steroids can prevent testicular atrophy, many athletes take HCG for two or three weeks in the middle of their steroid regimen. It is often observed that this is the time when the athlete makes the best progress in terms of gains in strength and muscle mass. The reason for this is clear. On the one hand, when taking HCG, the athlete’s testosterone level immediately increases by leaps and bounds, on the other hand, the steroids cause a high concentration of anabolic substances in the blood. Many bodybuilders, heavyweight lifters, and weight lifters report decreased sexual drive at the end of a difficult training cycle, immediately before or after a competition, and especially toward the end of steroid treatment. Those athletes who have used steroids in the past accept this fact, knowing that this is a temporary condition. However, those who use steroids year-round and may face psychological consequences or risk the end of a relationship should consider this setback when using HCG on a regular basis. In most cases, decreased libido and sperm production caused by steroids can be successfully cured by treatment with HCG.
Most athletes, however, take HCG at the end of a treatment to prevent a complete crash, meaning to make the best possible transition to natural training. A prerequisite for this is that the dosage of steroids is slowly and steadily reduced prior to ingestion of HCG. Unfortunately, although HCG induces a rapid and significant increase in endogenous plasma testosterone levels, it is not the perfect drug to prevent loss of strength and size at the end of steroid treatment. As is often observed, the athlete experiences delayed readjustment. Although HCG stimulates endogenous testosterone production, it does not help normalize the hypothalamic-pituitary system. The hypothalamus and pituitary gland are still in a contradictory state after long-term steroid use and persist while HCG is being used because the endogenous testosterone formed as a result of exogenous HCG suppresses endogenous LH production. After stopping HCG, the athlete must still go through a readjustment period. This is only delayed by the use of HCG. For this reason, experienced athletes often take Clomid and Clenbuterol after HCG intake or immediately start another steroid treatment. Some only take HCG to get off the steroids for two or three weeks.
Unfortunately, many bodybuilders still find that pre-contest HCG helps them get tougher or break down subcutaneous fat so that contours and blood vessels show up better. The HCG package insert makes it clear that HCG has no known effect on fat mobilization, appetite or hunger pangs, nor on the distribution of body fat. HCG has not been proven to be effective as an adjunctive therapy in the management of obesity, nor does it break down fat in addition to calorie restriction.
5000iu
Athletes should take 5000 I.U. inject. Since, as explained, testosterone levels remain significantly elevated over several days, there is no need to inject HCG more frequently than every five days. The relative dose is at the discretion of the athlete and should be based on the length of previous steroid use and the strength of the various steroid preparations. Athletes who are taking steroids for more than three months and those who predominantly use highly androgenic steroids like Anadrol, Sustanon Cypionate, Dianabol (D-bol), etc. should take a relatively high dose. The effective dose for athletes is usually 2000 – 5000 I.U. per injection and, as mentioned, should be injected every five days. HCG should be taken for a maximum of four weeks.
If HCG is taken in high doses by male athletes for several weeks, there is a possibility that the testicles will not respond adequately to subsequent HCG intake and the release of the body’s own LH. This can lead to permanent inappropriate sex gland function. HCG cycles should be kept low, around three weeks each, with a break of at least a month in between. For example, HCG can be used for 2-3 weeks in the middle of a cycle and then 2-3 weeks at the end of the cycle. It is speculated that overuse of HCG can permanently suppress the body’s gonadotropin production. For this reason, short cycles are the best choice.
THE SIDE EFFECTS OF HCG (HUMAN CHORIONGONADOTROPIN):
HCG can sometimes cause side effects similar to those of injectable testosterone. Higher testosterone production is also associated with increased estrogen levels, which can lead to gynecomastia. This can manifest itself as temporary breast growth, or in men it can increase existing breast growth. Therefore, far-sighted athletes combine HCG with an anti-estrogen. Male athletes also report more frequent erections and increased sexual desire. In high doses, it can cause acne and lead to mineral and water retention.
5000 I.U. /amp.
You must be logged in to post a review.





Reviews
There are no reviews yet.